

Setup
In order to interact with a given Gitlab instance through its REST API, u-sonar-status needs to be authorised and authenticated. To do so, together with Gitlab’s instance URL, an API token must be provided.
Pre-requisite
The key of the project in Sonar has to be: project_<project id> (example project_56)
-
You can access the GitLab project with:
<gitlab server>/projects/56(redirects you to the project page) -
You can access the Sonar project with:
<sonar server>/dashboard?id=project_56
GitLab: Generate an API Token
You will need a personal access token or a group access in order for the tool to interact with your repositories on GitLab.
All the actions are done using the REST API of GitLab.
You will need the api scope and a role allowed to post external status check (probably Maintainer).
Sonar: Generate an API Token
See documentation: Generating and using tokens
Application Setup
Depending on your setup you might need to set some configuration properties.
Minimal config entries:
Optional config entries:
And if you are on prem GitLab and Sonar servers:
SonarQube: Webhook Setup
In SonarQube you need to configure a webhook Webhook pointing to the location where u-sonar-status is available:
-
Name: Any name so that you recognize that the webhook was created for the
u-sonar-statustool. -
URL:
<server url>/u-sonar-status/sonar(you decide to point to the non-blocking or blocking endpoint) -
Secret:
<any value>if you set a value, you will need to configure sonarqube.webhook.secret
GitLab
As soon as the tool receives the first Sonar webhook, it will auto register the external status check.
You will see it under "Settings > Merge requests" of each project:
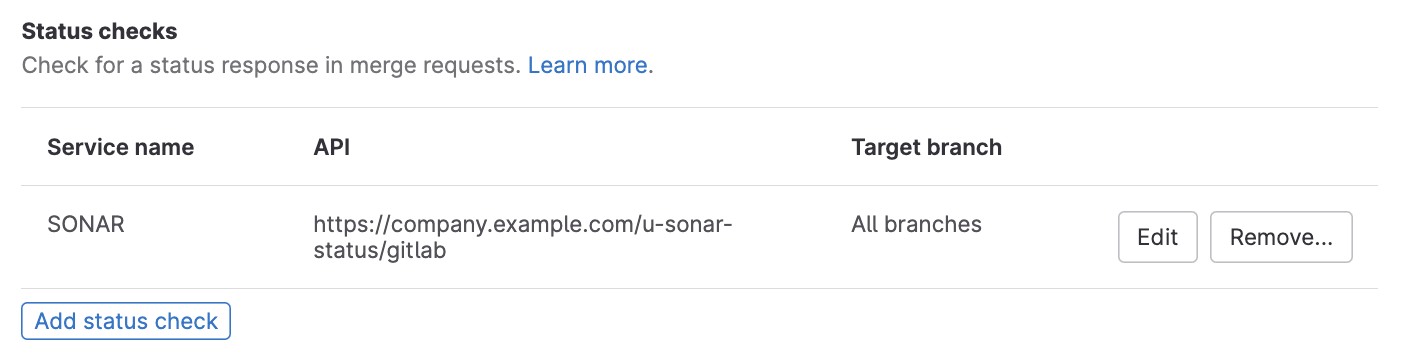
See the GitLab doc View the status checks on a project
Dev setup
The application can be started locally, check local build section.
Working with remote instances
If you are working locally with a remote sonarqube or gitlab instance (like https://sonarcloud.io/ or https://gitlab.com/), adding some proxy might be useful:
With a tool like ngrok you will get a public url (something like https://2a01-8943-19d-e0a-8b20-645f-f7a2-c2d-9be1.ngrok.io) that points to your localhost computer.
u-sonar-status is running locally on port 8080)ngrok http 8080
With a tool like mitmproxy you can proxy the remote instance to capture the REST requests made by u-sonar-status to the remote instance.
For SonarQube:
mitmproxy -p 8881 --mode reverse:https://sonarcloud.io
And then make u-sonar-status use localhost:8881 instead of sonarcloud.io directly:
export SONARQUBE_HOST=http://localhost:8881
For GitLab:
mitmproxy -p 8882 --mode reverse:https://gitlab.com
And then make u-sonar-status use localhost:8882 instead of gitlab.com directly:
export GITLAB_HOST=http://localhost:8882
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.